- HOME
- Technical Capability
- Facility
-

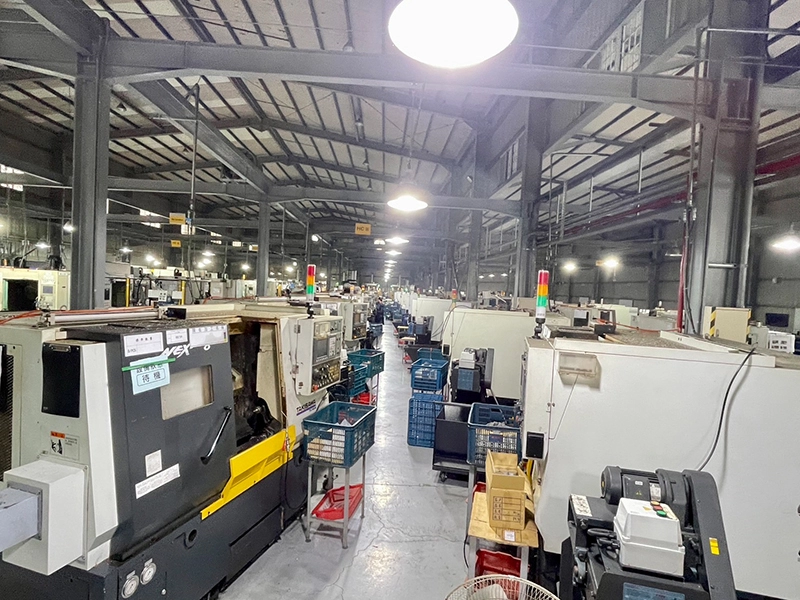
Facility
- CNC Tapping (Brother):82 sets
- CNC Tapping (FANUC):16 sets
- CNC Lathe (TAKISAWA):42 sets
- 4-axis Rotary Table (YUKIWA):78 sets
- 4.5-axis TILTING ROTARY (YUKIWA): 8 sets
- ABB Robot + Nachi Robot for tapping: 4 Lines
- Automation for Lathe:7 Lines
- 3D-CMM (SHEFFIELD D8,D12):3 sets
- 3D-CMM (Zeiss Contura G2) :1 sets
CNC Lathe:
In the CNC lathe machining process, the cutting tool is fixed to the lathe and rotates at high speed to remove material until the machining is completed. CNC lathes are widely used in various fields, including mechanical manufacturing, metal processing, and equipment maintenance. The components of a lathe include a cast iron frame, a tool post for planar cutting, various cutting tools, a drive system, and a control unit. The electric motor drives the entire system through belts, gears, cams, and turntables at different speeds, powering the entire drive system. The degree of automation varies among different lathes. When the lathe’s operation is controlled by a computer program, it is referred to as a CNC lathe.

Takisawa NEX108

Takisawa NEX110
CNC 4-Axis Tapping Center:
The four-axis machining center enhances precision and production efficiency by allowing the tool to perform both linear and rotational movements simultaneously. It is capable of accurately processing complex surfaces and three-dimensional structures, as well as precisely machining workpieces of varying sizes and types.
CNC 5-Axis Tapping Center:
Five-axis machining is an advanced CNC machining technology that adds an additional rotational axis compared to four-axis machining. This provides extremely high flexibility and precision, enabling the production of complex and highly accurate parts, such as aerospace components and medical devices. During operation, the five-axis machining center uses a computer numerical control (CNC) system to coordinate and control all five axes, each with its own independent controller and motor drive system, allowing for synchronized movement. It is primarily used in fields requiring the processing of multi-curved, high-precision parts.

4-Axis Tapping Center
(YUKIWA)
5-Axis Tapping Center
(YUKIWA)

Brother
S500X1/X2/Xd1
Brother
R450Xd1
FUNUC
D21LiA
Manufacturing Process Leveling:
This approach ensures that production processes flow smoothly without delays or interruptions, facilitating single-piece or small-batch production flow. It reduces the likelihood of bottleneck processes and minimizes wasted time and delays during the manufacturing process.